Google’s New MCP Servers Let AI Agents Plug Into Its Tools

▼ Summary
– AI agents struggle to reliably connect with external tools and data, requiring developers to build fragile, hard-to-scale connector systems.
– Google is launching fully managed MCP servers to make its services like Maps and BigQuery easily accessible to AI agents, aiming to solve this integration problem.
– These servers use the open-source Model Context Protocol (MCP), allowing them to connect with various AI clients like Gemini, Claude, and ChatGPT.
– The initiative integrates with Google’s Apigee API management, enabling existing enterprise security and governance controls to also apply to AI agents.
– The servers include security features like Cloud IAM and Model Armor and will expand to more Google services, starting with a public preview for enterprise customers.
The challenge of connecting AI agents to external tools and data is a significant hurdle for developers aiming to build truly capable assistants. Google is addressing this complexity by launching fully managed, remote MCP (Model Context Protocol) servers, designed to seamlessly integrate its core services like Google Maps and BigQuery into AI agent workflows. This initiative, following the release of the Gemini 3 model, aims to pair advanced reasoning with reliable, real-world data connections, transforming how enterprises deploy intelligent systems.
Developers often spend weeks constructing fragile, custom connectors to link AI agents with necessary tools. Google’s new approach simplifies this dramatically. Instead of complex engineering, a developer can now integrate a service by simply pasting a URL to a managed endpoint. This reduces setup from days to minutes and provides a scalable, governed foundation. The initial launch includes MCP servers for Google Maps, BigQuery, Compute Engine, and Kubernetes Engine, enabling use cases like an analytics assistant querying live data or an operations agent managing cloud infrastructure.
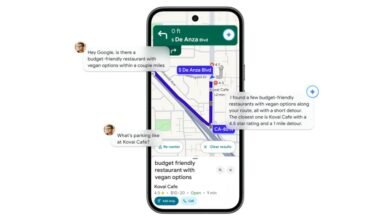
The practical impact is substantial. For instance, an AI agent planning a trip can move beyond relying on a model’s potentially outdated internal knowledge. By connecting to the Google Maps MCP server, the agent gains access to grounded, real-time location information, ensuring accuracy for directions, business hours, and traffic conditions. This shift from abstract knowledge to actionable tool use is central to creating effective agents.
These new servers are launching in a public preview, initially available at no extra cost to existing Google Cloud enterprise customers. While not yet under the full Google Cloud terms of service, the company expects a general availability release very soon, with plans to add more servers weekly. The protocol itself, MCP, is an open-source standard originally developed by Anthropic and recently donated to a Linux Foundation fund, promoting widespread adoption and interoperability.
A key advantage of using an open standard like MCP is compatibility. Because MCP is a standard, Google’s servers can connect to any compliant client. This includes Google’s own Gemini CLI and AI Studio, but also extends to third-party platforms like Anthropic’s Claude or OpenAI’s ChatGPT, creating a versatile ecosystem where tools and agents can freely interact.
For larger organizations, the strategic value connects to Google’s API management platform, Apigee. Many companies already use Apigee to secure and monitor their API traffic. Apigee can now translate a standard API into a discoverable MCP server, allowing existing product catalogs or internal systems to become tools for AI agents. Crucially, this applies the same security policies, quotas, and governance controls used for traditional applications to AI-driven interactions, a vital consideration for enterprise adoption.
Security is a foundational component of this rollout. Access to the MCP servers is governed by Google Cloud IAM (Identity and Access Management), providing precise control over what actions an agent can perform. Additionally, a specialized layer called Google Cloud Model Armor acts as a firewall for agentic workloads, designed to defend against novel threats such as prompt injection attacks or unauthorized data exfiltration. Administrators also have access to comprehensive audit logs for full observability into agent activity.
Looking ahead, Google plans to rapidly expand MCP support beyond the initial four services. In the coming months, developers can expect servers for areas including cloud storage, databases, logging and monitoring, and security tools. The overarching goal is to provide the essential infrastructure so development teams can focus on building innovative agent experiences rather than the underlying connectivity. By building this integrated plumbing, Google is positioning its cloud platform as a native home for the next generation of enterprise AI.
(Source: TechCrunch)