Google’s AI Model Tracks Climate Change Like a Satellite
▼ Summary
– Google’s new AI model, AlphaEarth Foundations, aims to analyze Earth’s changes using machine learning and decades of Google’s planetary data.
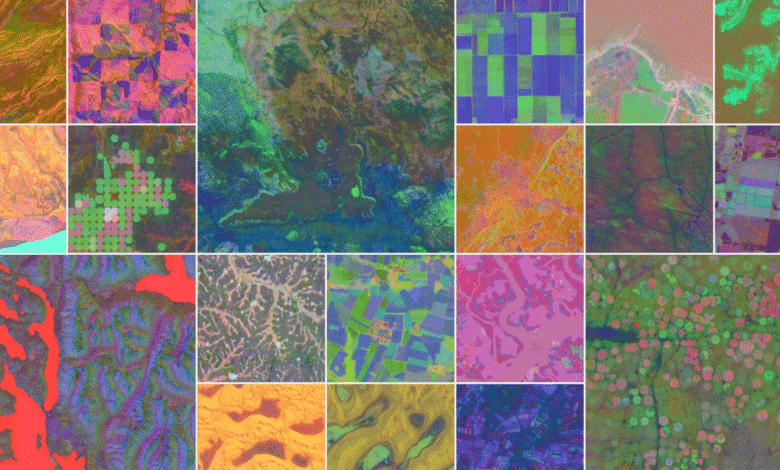
– The model uses “embeddings” to compress satellite data into color-coded maps showing material properties, vegetation, groundwater, and human constructions.
– It functions as a “virtual satellite,” providing on-demand detailed information about any location on Earth.
– The system helps users understand ecosystems by tracking air quality, sunlight, groundwater, and human projects to aid governments and corporations in decision-making.
– The model has already mapped Antarctica in detail and identified subtle agricultural land use variations in Canada.
Google’s latest AI innovation is transforming how we monitor and respond to climate change by analyzing Earth’s surface with unprecedented precision. This cutting-edge technology, developed by AlphaEarth Foundations, an extension of Google’s DeepMind, harnesses vast amounts of satellite data to create dynamic, high-resolution models of our planet’s ecosystems.
The system processes terabytes of daily satellite imagery, compressing it into manageable datasets while preserving critical details. Using a technique called “embeddings,” the AI overlays color-coded filters on maps to highlight everything from vegetation density and groundwater reserves to urban development and farmland. Essentially, it functions as a virtual satellite, offering real-time insights into environmental changes anywhere on Earth.
Beyond mapping, the technology aims to provide actionable intelligence for governments and businesses. By tracking shifts in air quality, sunlight exposure, and water availability, it helps identify optimal locations for agriculture, renewable energy projects, or infrastructure development. For instance, it could pinpoint regions with the highest solar potential or areas where crops would thrive based on groundwater accessibility.
Early tests have demonstrated remarkable accuracy, even in challenging environments like Antarctica, where inconsistent satellite coverage typically complicates data collection. The model has also detected subtle variations in Canadian farmland, changes invisible to conventional observation methods.
This tool represents a significant leap in environmental monitoring, offering a data-driven approach to tackling climate challenges. Whether optimizing resource allocation or planning sustainable development, Google’s AI could become an indispensable asset in the fight against ecological degradation.
(Source: Wired)




