Spot an AI Fake: 6 Telltale Signs & Free Detectors
▼ Summary
– AI-generated images are now pervasive online and are becoming increasingly difficult to distinguish from real photographs.
– Common visual flaws that can reveal an AI image include garbled text, anatomical errors like extra fingers, and an uncanny, hyper-realistic appearance.
– Other telltale signs are images that are overly chaotic or, conversely, lack detail and appear unnaturally smooth.
– Many small businesses are using AI to create logos and promotional images, which often look too perfect or contain illogical elements.
– Free tools like Google’s Circle to Search and Gemini can help detect AI images by checking for watermarks or analyzing the content.
The digital landscape is now saturated with artificial imagery, making it increasingly difficult to distinguish authentic photographs from convincing fakes. This flood of AI-generated content is not going to stop, and it’s only going to get harder to tell what’s real. As generative models improve daily, developing a critical eye for the subtle flaws in synthetic media becomes an essential skill. Fortunately, there are several common errors these systems still make, and a number of free tools can assist in the verification process.
One of the most persistent giveaways is garbled or nonsensical text. While AI image generators have improved, they frequently stumble when rendering letters on items like posters, book covers, or t-shirts. Zooming in often reveals warped characters, skewed alignment, or pure gibberish. Even with explicit instructions to retain text, the output can contain subtle distortions that betray its artificial origin.
Another classic red flag involves anatomical irregularities, particularly with hands and fingers. AI has a notorious history of creating people with extra digits, fingers that merge together, or missing knuckles. It’s wise to also examine other body parts for impossibly long necks, misplaced limbs, or facial features like a single nostril. While these errors are becoming less common, they remain a strong indicator of AI involvement.
Many AI-generated portraits exhibit an uncanny, hyper-realistic appearance that feels off. You might notice a vacant, dead-eyed stare, overly glossy or misaligned pupils, and skin that seems poreless and plasticky. Teeth may overlap unnaturally, and hair can appear too perfectly wispy. The overall effect is someone who looks digitally altered, possessing a flawless yet artificial quality that real photographs rarely have.
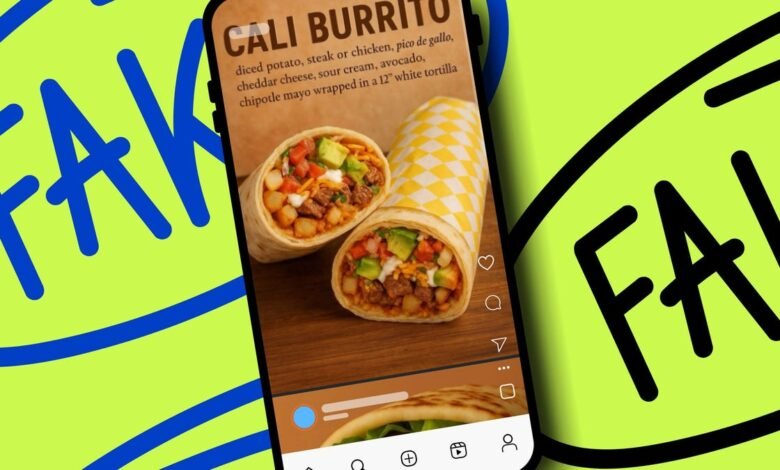
A surge in suspiciously polished marketing materials can also signal AI use. Suddenly, every local business appears to have a professional design team, producing logos, menus, and food photos that look illustrated. The food might glisten perfectly, with no drips or stains, appearing too uniform and clean. When a small restaurant’s social media features graphics rivaling a national ad campaign, it’s often a sign that generative AI, not a graphic designer, is behind the work.
Some AI images suffer from visual chaos and overwhelming detail. These pictures cram in strange, repeating textures, hyper-detailed backgrounds, and impossible lighting effects. Shadows may fall at illogical angles, and reflections might defy physics. The entire composition feels overloaded, as if a computer was instructed to include every dramatic element simultaneously, resulting in a confusing and artificial-looking scene.
Conversely, a lack of detail or overly smooth textures can also be a giveaway. This is especially apparent in AI-“restored” historical photos, where brickwork loses its granular texture and becomes a flat, red plaster. Leaves on trees may blur into a green mass, and people can resemble painted figures. The process often strips away the authentic, nuanced details that define a real photograph, leaving behind a simplified, illustrated version.
Beyond manual inspection, you can leverage free technology to help detect AI images. Google offers several integrated tools. On Android devices, the Circle to Search feature allows you to directly inquire if a photo is AI-generated. Google Lens provides an “About this image” context panel, which can indicate if an image carries an AI watermark like SynthID. Within the Gemini app, you can upload a photo and ask if it was created with Google AI; the system will check for watermarks and may use reasoning to make an educated guess. While these tools are not infallible and sophisticated fakes can sometimes bypass them, they provide a valuable, no-cost first line of defense.
(Source: ZDNET)





