
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has reshaped modern warfare, providing militaries with powerful tools that offer strategic advantages but also introduce complex ethical and operational challenges. Nowhere is this transformation more apparent than in the Israel-Gaza and Israel-Lebanon conflicts, where AI-powered systems drive both defensive and offensive strategies. This article explores AI’s impact on these conflicts, examining the capabilities, ethical implications, and broader geopolitical consequences of autonomous and semi-autonomous warfare.
The Growing Role of AI in Military Operations
Military powers, particularly the United States, China, and Russia, have made significant strides in AI-driven technologies, effectively initiating an AI arms race. Unlike traditional warfare tools, AI provides unprecedented advantages in terms of speed, precision, and adaptability, turning military strategy on its head. Automated drones, predictive analytics, and AI-augmented decision-making tools empower forces to respond swiftly to threats and seize the upper hand in real time.
Among AI’s contributions to warfare, four major applications stand out: autonomous weapon systems (AWS), surveillance and reconnaissance operations, cyber warfare, and logistics. Each area showcases AI’s ability to augment military effectiveness, but also underscores the risks of minimizing human oversight in conflict scenarios.
- – Autonomous Weapon Systems (AWS): Systems like Israel’s Iron Dome showcase AI’s ability to independently select and engage targets, surpassing human reaction times in defensive operations. However, this automation raises critical questions about accountability when algorithms make life-and-death decisions.
- – Surveillance and Reconnaissance: AI-driven systems enable real-time analysis of vast data streams, improving target identification and situational awareness. This capability has proven crucial in recent conflicts, though it raises concerns about privacy and civilian protection.
- – Cyber Warfare: AI enhances both offensive and defensive cyber capabilities.
- – Logistics: AI optimizes military planning and resource allocation.
AI in Contemporary Conflicts: A New Era of Warfare

The use of AI in warfare is no longer theoretical. Its impact can be seen in multiple ongoing conflicts, each providing case studies in both the potential and peril of AI in military contexts.
- – Ukraine-Russia Conflict: Ukraine has used AI to boost its defense capabilities, particularly through autonomous drones designed to strike Russian assets with pinpoint accuracy. This has provided Ukraine with a crucial edge, demonstrating how smaller nations can leverage AI to compensate for traditional military imbalances.
- – Libyan Civil War: Armed drones with autonomous targeting capabilities were reportedly used in Libya, marking one of the first cases of such technology in combat. These drones’ capacity to operate independently has introduced ethical and legal questions, especially concerning their use in populated areas without human oversight.
- – U.S. Project Maven: In Yemen, the United States has employed AI to enhance surveillance through Project Maven, an initiative that uses machine learning to identify and track potential threats. While the project underscores AI’s efficiency in conflict zones, it has also stirred ethical debates over the reliability and accountability of AI in high-stakes situations.
These instances highlight AI’s tactical advantages but also emphasize the risks, particularly in conflicts with complex human dynamics. Autonomous systems can escalate conflicts in ways unforeseen by human strategists, and with the increasing reliance on AI, the possibility of errors or unanticipated consequences grows.
AI in the Israel-Gaza Conflict
Israel has heavily integrated AI into its military operations in Gaza, particularly through its “Lavender” AI system, which has been instrumental in identifying potential Hamas targets. This system represents one of the most extensive uses of AI-driven surveillance and targeting, prompting some analysts to refer to recent hostilities as the world’s first “AI war“.
1. Lavender AI System: Precision and Ethical Concerns

The Lavender AI system has identified over 37,000 potential targets linked to Hamas within Gaza, reflecting the capability of AI to process large data sets for rapid targeting. The system analyzes input from drones, satellites, and ground-based intelligence sources to identify patterns and quickly flag targets. This system theoretically enables Israel to distinguish between civilians and combatants, enhancing both precision and speed.
However, Lavender’s high-stakes deployment has led to considerable ethical concerns. The system reportedly operates with a 10% error rate, leading to the destruction of civilian infrastructure and raising the risk of non-combatant casualties. This margin for error is significant in densely populated areas, where collateral damage could inflame tensions and undermine humanitarian protections. There have been accusations that Israel’s military relies on Lavender’s outputs as if they were human decisions, which could lead to further erosion of accountability when civilians are affected.
2. Iron Dome and Other AI-Enhanced Defense Systems
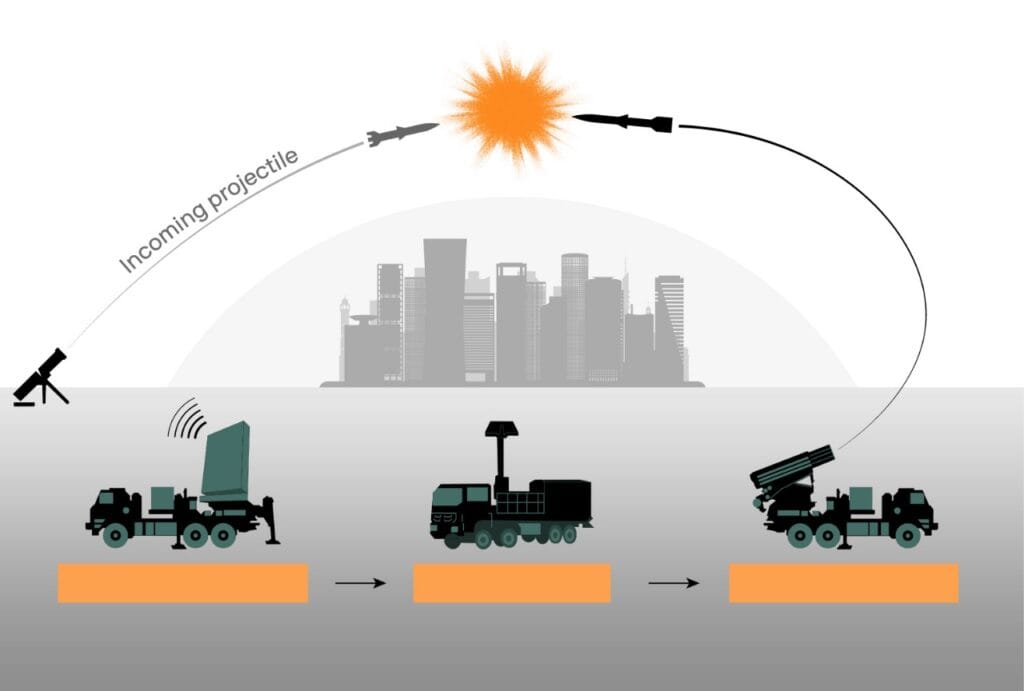
In addition to the Lavender system, Israel employs the Iron Dome, a semi-autonomous missile defense system. Equipped with AI algorithms, the Iron Dome has been instrumental in intercepting thousands of rockets from Gaza, only targeting projectiles expected to impact populated areas. This sophisticated system, powered by machine learning, allows Israel to defend against missile attacks with high efficiency, conserving resources and minimizing human intervention.
The integration of AI into Israel’s defense arsenal highlights its advantages in accuracy and responsiveness, but it also presents significant ethical questions. The reliance on AI for quick decision-making in high-pressure situations has the potential to reduce human oversight, especially in cases involving civilian lives. The cumulative effects of these systems underscore the ethical complexities associated with AI’s expanding role in combat zones
AI in the Israel-Lebanon Conflict
While AI’s usage in the Israel-Gaza conflict is widely discussed, its role in the Israel-Lebanon conflict is also significant, albeit less publicized. Israel’s defense strategy regarding Lebanon, particularly against Hezbollah, heavily relies on AI-driven surveillance and targeting systems. The border between Israel and Lebanon is frequently monitored by sophisticated AI systems designed to detect suspicious movements and activities, providing Israel with advanced situational awareness.
1. Border Surveillance and Monitoring

The Israel-Lebanon border is one of the most fortified in the world, with Israel using a network of AI-driven sensors, cameras, and aerial drones to monitor activities across the border. These systems employ machine learning algorithms to analyze movement patterns and identify potential threats in real time. By processing data from multiple sources, including thermal imaging and radar, AI algorithms assist Israeli forces in distinguishing between civilians and suspected militants, allowing them to respond swiftly to any perceived threat.
Israel’s use of AI for border surveillance provides several advantages: it helps prevent infiltrations, detects potential attacks before they escalate, and supports strategic planning by providing real-time intelligence. However, the use of AI on this scale in border surveillance has also raised privacy concerns, as it impacts not only military personnel but also civilians on both sides of the border. Critics argue that the data collected by these AI systems could be misused, leading to unintended consequences in an already tense region.
2. Predictive Analytics and Targeting
In its engagements with Hezbollah, Israel has increasingly utilized predictive analytics powered by AI to anticipate potential threats and preemptively neutralize them. This approach involves analyzing historical data, current intelligence reports, and behavioral patterns to identify likely targets or areas where attacks may originate. Predictive AI algorithms aid Israel’s military forces in allocating resources more effectively and preparing defenses in advance of potential Hezbollah incursions.
AI’s role in predictive analytics is particularly valuable in the Israel-Lebanon conflict, where Hezbollah often operates in highly concealed and strategically advantageous positions. AI-driven data analysis provides Israel with the insights needed to make proactive decisions and reduce the risk of surprise attacks. However, these predictive measures carry the risk of over-reliance on algorithmic outputs, which, despite their sophistication, are not infallible. Mistakes in predictive targeting could lead to the loss of innocent lives, which would further complicate the conflict and strain diplomatic relations.
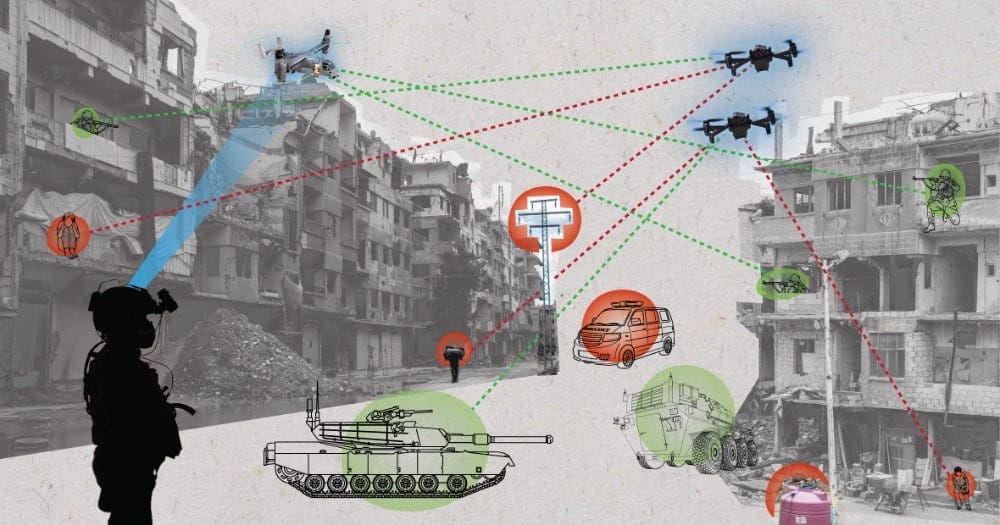
Broader Ethical and Strategic Concerns
The increasing autonomy of AI in warfare demands urgent consideration of its ethical and legal ramifications. The deployment of AI systems, like Lavender in Gaza, illustrates a fundamental shift in warfare where human oversight may be partially or wholly replaced by machine decision-making.
1. Error Margins and Accountability
The 10% error rate associated with Lavender’s targeting decisions in Gaza underscores the challenges of accountability in AI-driven warfare. While AI systems offer unmatched efficiency, their reliance on algorithms without moral reasoning makes them susceptible to significant errors, especially in complex urban settings. In cases of civilian casualties, attributing responsibility becomes difficult when decisions originate from autonomous or semi-autonomous systems. These complexities emphasize the need for regulatory measures to oversee AI’s role in targeting and engagement protocols.
2. Privacy and Civil Liberties in Surveillance
The extensive use of AI in border surveillance along the Israel-Lebanon boundary raises important privacy concerns, as civilians in monitored areas may face unwarranted data collection. The potential misuse of this data could have long-lasting implications, both for individual privacy rights and for the broader human rights landscape. Effective regulation is essential to ensure that AI-based surveillance respects civil liberties, especially when deployed in areas with substantial civilian populations.
3. Escalation Risks in the AI Arms Race
The rapid adoption of AI-driven systems in Israel and other global powers highlights a broader trend: the AI arms race. As countries invest in increasingly advanced technologies, the risk of escalation rises. Unlike previous arms races, AI introduces unknown risks, particularly because autonomous systems may behave unpredictably in complex scenarios. Establishing international norms and agreements for AI’s use in warfare could mitigate these risks, preventing destabilizing consequences in high-stakes conflicts.

Moving Toward Responsible AI in Warfare
AI’s role in the Israel-Gaza and Israel-Lebanon conflicts illustrates both its tactical advantages and the pressing ethical dilemmas it brings to modern warfare. While AI enhances military precision and decision-making speed, it also risks compromising civilian safety and eroding accountability. Addressing these challenges requires a proactive approach, as the international community must develop legal and ethical frameworks that establish clear boundaries for AI use in combat.
As AI continues to influence the battlefield, balancing innovation with responsibility will be critical. Effective regulation that prioritizes accountability, transparency, and human oversight is essential to ensure that AI technologies serve their intended purpose without compromising fundamental human rights. By addressing these ethical and strategic concerns, the global community can foster a more responsible future for AI in warfare, preserving human control in an increasingly automated world.






